| Jellyfish Quick Facts |
| Name: |
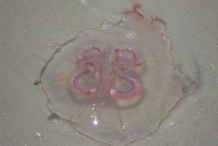
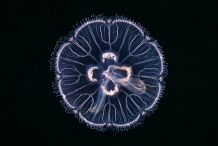
Jellyfish |
| Scientific Name: |
Aurelia aurita |
| Colors |
Clear, pink, blue, yellow and purple |
| Shapes |
Bell shaped |
| Calories |
21 Kcal./cup |
| Major nutrients |
Manganese (1065.22%)
Sodium (374.67%)
Iron (16.50%)
Choline (10.02%)
Copper (9.00%)
|
| Health benefits |
Cut off weight, Build memory, Prevent brain related problems, Promote cognition, Reverse aging |
Jellyfish is carnivorous feeding variety of planktonic species such as crustaceans, molluscs, copepods and young worms. Plankton is taken in a layer of mucus covering jellyfish. The body of jellyfish has tiny hair like structures producing currents by beating. Currents transfers captured plankton towards edge of bell where it is discarded with arms and passed to mouth. Tentacles around margins of bell or arms bear stinging cells that are used occasionally for catching other prey and small fishes. They have separate sexes and fertilization is occurred internally. The sperm is taken into female body by mouth. Fertilized eggs are subjected to undergo development in pockets in arms which surround the mouth. During autumn the free swimming larvae are released and after some time, they settle and forms into tiny sessile animals that reproduce asexually and release free swimming miniature immature jellyfish known as ephyrae feeding on plankton and becomes mature after three months. Mainly they are free swimming marine animals having umbrella shaped bells and trailing tentacles. Bell can beat for providing propulsion and efficient locomotion. Their lifecycle is complex. Normally medusa is sexual phase; planula larva could disperse widely and is followed by sedentary polyp phase.
They could be found all over the world to the deep sea from the surface waters. Exclusively, scyphozoans are marine but some are hydrozoans having similar appearance living in freshwater. Jellyfish are large and colorful being common in coastal zones worldwide. Most of the species of medusa gets mature within few months, are fast growing and die soon after breeding but polyp stage that are attached to seabed have long life. They have roamed seas for somewhat 500 million years and may be possibly 700 million years or more that makes them oldest multi-organ animal group.
In certain cultures, jellyfish are consumed by humans as delicacy in some Asian countries. The species of Rhizostomae are pressed and salted to eliminate excess water.
Body system
Aurelia does not possess respiratory parts such as lungs, gills and trachea. Being a small organism, it respires by diffusing oxygen from water through thin membrane. Within gastrovascular cavity, high oxygenated water can come in and low oxygenated water can be expelled by ciliated action by promoting diffusion of oxygen through cell. Aurelia is supposed to diffuse more nutrients and oxygen to cells by large surface area membrane to volume ratio.
Aurelia has a basic body plan consisting of several parts. Animal has the shortage of excretory, respiratory and circulatory systems. Adult medusa of Aurelia has transparent look with umbrella margin membrane and tentacles being attached to bottom. They have 4 bright circular gonads which are under stomach. The food is passed through muscular manubrium and radial canals helps to disperse food. There is middle layer of gastroderascular, mesoglea cavity having gastrodermis and epidermis. It has a nerve net which is responsible for contraction in swimming muscles and also feeding responses. Adult ones could measures upto the diameter of 40 cm.
Young during larval stage, planula, contains small ciliated cell and after freely swimming in plankton for a day or more, it settles on applicable substrate where it transforms into special type of polyp known scyphistoma that divides by strobilation into small ephyrae swimming off for growing as medusae. The increasing size is less than 1 m in planula stage and upto 1 cm in ephyra stage and then to several cm in diameter in medusa stage.
Locomotion
They are considered to be the most energetic and efficient swimmers. They move through water by expanding and contracting radially its bell shaped bodies in order to push water behind them. It pauses between expansion and contraction for creating two vortex rings. They use muscles to contract body that sheds first vortex and pushes animal forward. Mesoglea is elastic which assist the expansion to be powered exclusively by relaxing bell releasing stored energy from contraction. Doing so, 2nd vortex ring rolls under it and starts to spin faster. It sucks in water that refills bell and pushed up against center of the body providing it secondary or free boost forward. This mechanism is known as passive energy recapture and works at low speeds and also relatively small body sizes that allows animal to drive 30 percent farther on each swimming cycle. They achieve 48 percent lower cost of transport in comparison to other animals in similar studies.
Reproduction
Jellyfish contains separate sexes i.e. they are either female or male. For reproduction, male and females release sperm and eggs into water for sexual reproduction. They develop larvae after fertilization which results into new jellyfish and settle in the sea bottom as polyps. By means of asexual reproduction, this polyp helps to develop new free living jellyfish.
Feeding
These species feed on plankton which includes organisms such as crustaceans, mollusks, rotifers, tunicate larvae, protozoans, young polychaetes, fish eggs, eggs, diatoms and other small organisms. They also feed on gelatinous zooplankton such as ctenophores and hydromedusae. Both larvae of Aurelia and adult medusae have nematocysts for capturing prey and in order to protect themselves from preadators. Foods are tied with mucus and are passed down by ciliated action down into gastrovascular cavity where serous cell digestive enzymes break down food. There is limited information about the need for particular minerals and vitamins but because of the presence of some digestive enzymes we could deduce in general that Aurelia aurita can process proteins, carbohydrates and lipids.
Predators
Aurelia aurita is are the prey of Ocean Sunfish (Mola mola), the scyphomedusa Phacellophora camtschatica, the Leatherback Sea Turtle (Dermochelys coriacea) and very large hydromedusa (Aequorea victoria). Sea birds fed upon moon jellies.
History
Jellies are regarded as one of the oldest animals on Earth, with a history dating back between 500 and 700 million years. They are the first known animal having nervous system which makes it an important step in evolution of life.
Types of Jellyfish
Within the phylum of Cnidarians, it is possible for differentiating four large groups, each with its own characteristics. They are as follows:
They alternately show the phases of polyp and jellyfish. Generally, they are small in size and could be solitary or colonial. This class includes siphonophores. It is floating colonies of polyp individuals or jellyfish having abundant poisonous cells which are used for self-defence and in some cases, it could be harmful for people. Siphonophores form complex colonies of individuals who are specialized in various functions. Some serve as flotation organ and others for defence, nutrition and for feeling. Portuguese men of war (Physalia physalis) or By-the-wind sailor (Velella spirans) are the best known species that could cause painful burns for bathers and even heart failure.
This group is known as true jellyfish. Normally, they are great marine jellyfish having very short and even non-existent polyp phase. Species such as mauve stinger or purple jellyfish could be striking really on night time drive. It has eight stinging tentacles which could measure ten meters in diameter when spread out.
It inhabits in water of tropical and sub-tropical seas. It is also known as sea wasps and box jellyfish. They possess umbrella in form of cube having four sides. Their sting is so powerful an may cause even death in just few minutes if not treated with an antidote.
It includes madreporas, corals, sea anemones and actinias. Generally these species have beautiful color. Some live in isolation such as beadlet anemone (Actinia equia), some anemones such as Cerianthus membranaceus (colour tube anemone) and other such as red gorgonians (Paramuricea sp.) and corals form colonies.
Health Benefits of Jellyfish
Jellyfish contains calcium binding proteins which are helpful to maintain healthy cells and is considered an age fighting solution and is also good for human brain. It has collagen that maintains firm and young skin. Let’s learn more about the health benefits of Jellyfish:
- Cut off weight
The presence of low calories with significant carbohydrate makes it an excellent choice for making weight loss diet. In fact, it is a great source of protein which assists to maintain healthy muscle during diet and amino acids assist in continuation of cell regeneration.
- Build memory
Jellyfish is a type of seafood which is beneficial for memory. This sea creature has calcium binding protein in remarkable amounts. This protein is produced by brain itself but as the people ages, its production is reduced progressively.
- Prevent brain related problems
As mentioned from the previous point, the same calcium binding protein content found in jellyfish is also good to reduce the risk of several brain diseases which is aging related but also some fatal conditions such as Alzheimer and dementia.
- Promote cognition
Beside its benefit for brain, calcium binding protein is beneficial for counteracting age associated cognitive decline because nerve system in the brain should be well maintained. The consumption of jellyfish helps to optimize the regeneration of cells in the brain which also includes nerve system.
- Reverse aging
Jellyfish is known as immortal creature being able to fix itself. Though the consumption of jellyfish does not makes one immortal but slows down the aging process.
- Impressive amounts of collagen
Mentioned previously that jellyfish keeps one look younger due to the presence of collagen in jellyfish. Human body also normally produces collagen through the metabolism process of Vitamin C. The consumption of jellyfish makes the one to reap all the benefits in it.
- Skin appearance
Collagen is much beneficial for maintaining skin health. It assists in keeping elasticity of skin even when getting older. Collagen helps to support the regeneration of skin cells for keeping it firm and young for longer time.
- Added to cosmetics
Jellyfish is used as vital cosmetic ingredients due to its content of collagen. This creature has the ability to transform old cells into younger cells.
- Makes heart healthy
Jellyfish has low content of calories and carbohydrates and is loaded with amino acids and protein. Jellyfish is beneficial for heart. Jellyfish is safe seafood for those having heart problem.
- Lowers high blood pressure
Jellyfish is able to lower symptoms of high blood pressure. It helps to lower health risk associated with high blood pressure such as stroke and heart attack.
- Normalize blood pressure
Jellyfish is able to maintain the level of blood pressure and prevents hardening of arteries for maintaining healthy blood vessel.
How to Eat
- It is processed into dried product.
- Jellyfish is used in preparing sushi, salads, main courses and noodles.
- In Asian countries such as Korea, China, Vietnam, Taiwan and Japan, pickled and dehydrated jellyfish are regarded as delicacy.
- Jellyfish salad is made by using cold marinated jellyfish which is thinly sliced.
- In Thailand, jellyfish is used for making crunchy style noodle.
Precautions
- Jellyfish stings could be painful and even dangerous to humans. The stings occur accidently not purposely.
- The symptoms of jellyfish stings include itching, stinging or intense pain, raised welts and rash.
- Vomiting, nausea, lymph node swelling, diarrhea, abdominal pain, muscle spasms and tingling/numbness are its progressive effects.
- People might experience coma, difficulty breathing and even death as severe reactions.
- It should be consumed in dried form because jellyfish is decayed within few hours and is very toxic.
Other Facts
- Jellyfish are termed as non-aggressive, free swimming and gelatinous marine animals with tentacles.
- Tentacles are covered with nematocysts (sacs) which are loaded with venom (poison) and its sting might be painful to sometimes life threatening.
- The family includes marine animals such as box jellyfish, jellyfish, hydroids, Portuguese man-of-war, fire coral, anemones and hydroids.
- Jellyfish could be found throughout the world and deadly ones are found in Australian and Indo-Pacific waters.
- Usually, jellyfish are found near water surface during diminished light floating in water column.
- Over 200 types of jellyfish are documented.
- Often they could be translucent or transparent.
- The group of jellyfish is known as swarm, bloom and smack.
- They do not have brain.
References:
http://www.thecephalopodpage.org/MarineInvertebrateZoology/Aureliaaurita.html
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=51701#null
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jellyfish
https://kids.nationalgeographic.com/animals/jellyfish/#jellyfish-tentacles.jpg
https://www.emedicinehealth.com/jellyfish_stings/article_em.htm#how_can_i_prevent_jellyfish_sting
http://wiki.safariltd.com/index.php/Jellyfish
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jellyfish_as_food
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/sciencefacts/animals/jellyfish.html
https://drhealthbenefits.com/food-bevarages/food/seafood/health-benefits-jellyfish
Comments
comments