| Butternut Quick Facts |
| Name: |
Butternut |
| Scientific Name: |
Juglans cinerea |
| Origin |
Native to Southeast Canada and Eastern United States. |
| Colors |
Green |
| Shapes |
Oblong to ovoid, 3 to 6 cm long |
| Calories |
734 Kcal./cup |
| Major nutrients |
Manganese (342.26%)
Total Fat (195.37%)
Tryptophan (99.77%)
Valine (87.55%)
Isoleucine (84.63%)
|
Butternut with its scientific name Juglans cinerea, is a deciduous tree belonging to walnut family called Juglandaceae and is native to Southeast Canada and Eastern United States. Periodically, Butternut is cultivated for the edible seeds produced by the species by the people of North America. Sometimes, butternut is cultivated for its timber in Denmark and Romania. Other common names from which Butternut is known by are: White walnut, Butternut, Lemon walnut, Butternussbaum, Nogal Blanco Americano, Douberre, Nogal Ceniciento, Noyer à Beurre, Noyer Blanc, Noyer de Beurre, Oil Nut and Noyer Cendré. Butter is also known as white walnut due to its light colored wood which have natural golden luster becoming satin like when polished. As the wood is moderately hard, it could be carved and sawed easily. It is used for making cabinetry, furniture, interior woodwork, instrument cases including church decoration, altars and hand carved wall panels and trim.
Butternut prefers well drained soils and grows well on stream banks. It is a deciduous tree which grows up to the height of 40 to 60 feet tall having an open broadly to rounded crown. The tree bears odd to pinnate compound leaves each measuring 20 inches long having 11 to 17 oblong to lanceolate leaflets. Flower appears during late spring, female flowers form in short terminal spikes and male flowers in drooping catkins. Female flowers are replaced by ovoid to oblong nuts which is encased in hairy indehiscent husks. The shells of nut are hard to crack and have small kernels which are tasty, oily and sweet with buttery flavor. The tree bear fruit after six to ten years of seeds sown and fruit is usually produced biennially. The trees of Butternut survive for short time period in comparison to other trees and are found rarely to grow beyond 80 years.
Butternut is used by the people for gallbladder disorders, constipation, skin diseases and hemorrhoids. It is also used to treat infections caused by parasites and bacteria as well as cancer. In herbal medicine, butternut is used as an essential drug for treating persistent constipation that assist to promote regular bowel movements. It also effectively lowers the LDL cholesterol level by promoting the eradicating of water materials in liver that lowers the burden on liver. The preparation of inner bark infusion is used in form of colagogo, febrigugo, stomach and mild laxative. When this infusion is used in small doses, it is found to be very effective.
Plant
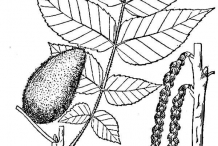
Butternut tree is small to medium sized native trees having stiff upright branches and wide spreading crown. Leaflets have sticky to oily hairs to touch. Terminal buds measures 12 to 18 mm long. The tree has thick, brownish to gray bark which is shallowly divided into smooth or scaly plates. It has pinnately compound leaves. Leaflets are ovate to lanceolate or oblong to lanceolate leaflets measuring 5 to 11 cm long having finely toothed margins. The lower surfaces are covered with stellate hairs. The tree bears unisexual flowers: male (staminate) and female (pistillate). Female flowers grow in terminal clusters of 6 to 8 flowers each and male flowers are in slender catkins of 6 to 14 cm long. Flowers are replaced by oblong to ovoid nut which is 3 to 6 cm long and 2 to 4 cm broad found single or in 2 to 5 clusters having thick, hard and deeply furrowed shell which is enclosed by a thick husk having sticky glandular surface.
Fruit
Fruit is the nut in lemon shaped which is formed in the bunches of two to six. Nut is oblong to ovoid, 3 to 6 cm long and 2 to 4 cm broad which is surrounded by a green husk before it gets mature.
Flower
The tree bloom flowers from April to June. Staminate (male) flowers are yellow to green, inconspicuous, slender catkins which forms from auxiliary buds. Pistillate (female) flowers are short terminal spikes and have light pink stigma. Flowers of both sexes do not mature together on any individual tree.
Twig
Twigs are stout, pubescent, yellow to brown to gray having chambered pith which is dark brown. It has large buds which are covered with light colored pubescent scales. Leaf scars are three lobed which resembles monkey face. On the above of leaf scar, it has tuft of pubescence which resembles an eyebrow.
Traditional uses
- The bark possesses mild cathartic properties.
- The extract made from inner bark of the tree is used for preventing small pox and cure dysentery, intestinal and stomach discomfort.
- North American Indian tribes use Butternut for treating various conditions such as arthritic and rheumatic joints, dysentery, headaches, wounds and constipation.
- It is useful for chronic constipation and promotes regular bowel movements.
- It reduces the cholesterol levels and enhances clearance of waste products by liver.
- Infusion prepared from inner bark is used for treating cramps.
- An infusion made from dried outer bark is useful to treat dysentery and toothache.
- Oil extracted from nuts is helpful for fungal infections and tapeworms.
- Butternut is used for hypatic congestions and dysentery.
- It is also used to treat herpes circinatus, acne, impetigo, rupia, chronic scaly skin, prurigomoluscum, lichen, pemphigus and chronic scaly skin.
- It is also used to cure mouth ulcers followed with constipation, mouth ulcers and sore mouth.
- An extract made from inner bark of walnut tree is used for preventing smallpox.
Precautions
- It contains naphthoquinone constituents which might cause irritation to stomach. So people with gallstones should avoid it.
- Butternut might cause irritation of intestines or stomach and diarrhea.
- Pregnant women should use it in moderate amounts because it might cause too much stimulation of bowels.
How to Eat
- In New England, it is used for making maple butternut candy.
- Seeds are consumed raw.
- Ground the seed into powder and use it with flours to make biscuits, cakes, bread and muffins.
- Pickle the unripe fruits.
- Oil could be extracted from seeds.
- Crushed nuts are used in puddings, breads and sauces.
- Oil is used to enhance the flavor of dishes.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=19250#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/54022/
http://www.pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Juglans+cinerea
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/29047
http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?kempercode=a874
https://www.botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/b/butnut98.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Juglans_cinerea
http://blog.emergencyoutdoors.com/wild-edible-plants-butternut-juglans-cinerea/
http://www.aihd.ku.edu/foods/Butternut.htmls
http://www.tipdisease.com/2015/07/butternut-juglans-cinerea-overview.html
http://healthnbeautyarticles.blogspot.com/2015/07/butternut-juglans-cinerea-overview.html
Comments
comments