| Wild cucumber Quick Facts |
| Name: |
Wild cucumber |
| Scientific Name: |
Cucumis anguria |
| Origin |
Africa and occurs from the woodlands of Angola and Zimbabwe to Namibia, Botswana and South Africa |
| Colors |
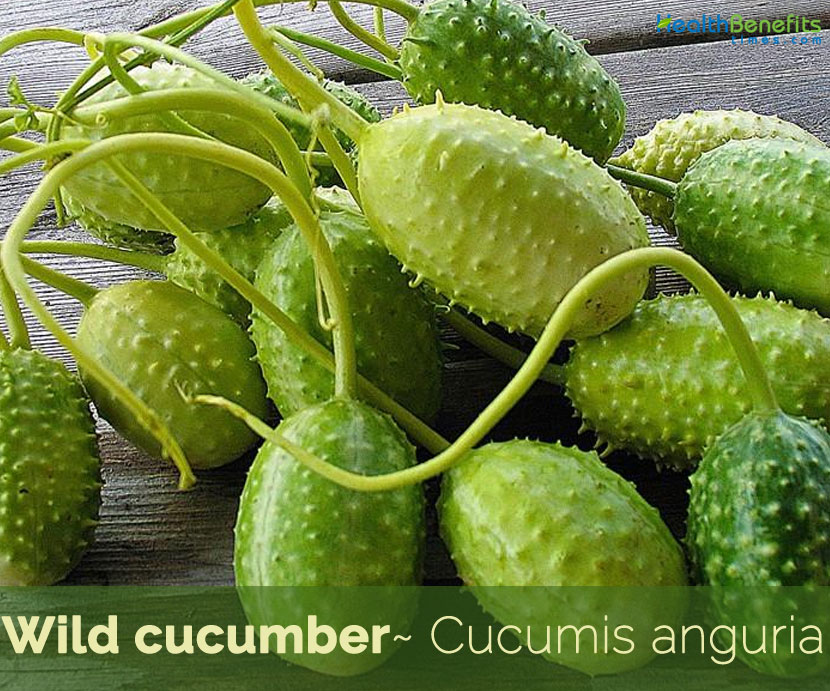
Initially greyish green with green stripes, ripening to yellowish as they matures |
| Shapes |
Ellipsoid to sub globose berry, 3–5 cm long, 20–30 mm diam. on a stalk 2.5–21 cm long |
| Flesh colors |
White or green flesh |
| Taste |
Mild taste, likened to a cross between a cucumber and a zucchini |
| Health benefits |
Beneficial for hemorrhoids, kidney stones, edema, stomach troubles, freckles, ringworm and jaundice |
Cucumis anguria, commonly known as Wild cucumber, cackrey, maroon cucumber, West Indian gherkin, and West Indian gourd, is a vine belonging to Cucumis L. (melon) genus and Cucurbitaceae (Cucumber family). The plant is native to Africa and occurs from the woodlands of Angola and Zimbabwe to Namibia, Botswana and South Africa. It is similar and related to the common cucumber (C. sativus) and its cultivars are known as gherkins. It is an important cucurbit vegetable and conventional medicinal crop. Few of the popular common names of the plant are Gherkin, cackrey, maroon cucumber, West Indian gherkin, West Indian gourd, Bur cucumber, Cassongo, Chikanyanga, Chikopa, Chipokolo, Goareberry gourd, Ingolowe, Jerusalem cucumber, Kasongwe, Muchacha, Muhawa, Prickly fruited gherkin, West Indian gourd, Burr gherkin, Jerusalem cucumber, Wild cucumber and wild spiny cucumber.
The fruits and leaves of wild cucumber are consumed as boiled, fried, stewed, pickled and also used as fresh in salads and hamburgers. Additionally, the fruits, roots and seeds are used for traditional medicine to treat stomach ache, jaundice, hemorrhoids and preventing stone formation in the kidney. Since there is a growing worldwide demand for pickled gherkins, many food companies have started to explore opportunities for producing gherkins. The plant is harvested from the wild, or more commonly cultivated, for its edible fruits and leaves and also for various medicinal uses. The fruits are often traded.
Plant Description
Wild cucumber is a thinly stemmed, annual monoecious herbaceous vine that grows about 3 meters long. The plant is found growing in semi-deciduous and deciduous woodland, tree and shrub savanna, grassland, semi-desert, wooded grassland, on Kalahari sand, abandoned cultivated land and near cattle kraals. The plant requires deep and well-drained soils such as white, red or brown sand, grey or red loam and gravelly or stony soil. It is also found on brackish soils with underlying limestone formations as well as blackish clay soil and grow well on seasonally moist alluvial soil. Trailing or scandent stems with bristle-like hairs grows up to 2 meters long, either scrambling over the ground or climbing into other plants, where they support themselves by means of tendrils.
Stem
Stems is annual, up to more than 2 m long, finely ridged, roughly whitish hairy, usually prostrate, but will climb on bushes and other support.
Leaves
The leaves are alternate and variable and tendrils are almost always present It is 4–8 cm long, 4–7 cm wide, deeply 5-lobed, the central lobe often 3-lobed, bristly, margins toothed. The leaves are large and lobed, resembling maple leaves in shape. Petiole is 2–6 cm long with spreading hairs.
Flower
Wild cucumbers have both male and female flowers. The male flowers sprout in round clusters about (10-20 cm) across with individual flowers (1 cm) wide. They have six thin petals. A single female flower is found at the base of a male flower stalk. The flowers are mostly unisexual and white or yellow in color they occur on the same plant (monoecious) or on separate plants (dioecious). Male flowers are fascicled, very small, and much shorter than the hispid petiole, whereas female flowers have longer peduncles. Flowering normally takes place from July to September.
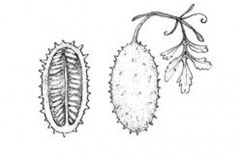
Fruit
Fertile flowers are followed by an ellipsoid to sub globose berry with one to many, often flattened seeds. It is 3–5 cm long, 20–30 mm diam. on a stalk 2.5–21 cm long. Fruits are initially grayish green with green stripes, ripening to yellowish as they matures and turn brown when dry before the fruit burst for seed collection. The inner flesh of the fruit is a white-green, and is crisp, crunchy texture. It has a mild taste, likened to a cross between a cucumber and a zucchini, with sweet and sour, slightly citrusy notes. Each fruit is filled with numerous tiny, tart edible seeds. As the fruit matures, it develops a strong tart and bitter taste while the outer flesh turns tough, and develops long, rubbery spines that eventually turn into spikes. The fruits of this species, often small, prickly and striped, were pickled and preserved in Old Cape kitchens.
Seeds
Seeds are ellipsoid, 4.5-5.2 mm long, 2-2.3 mm wide and 0.9-1.1 mm thick, compressed with rounded margins, smooth. The seeds are green in color when unripe and turn red when ripe, and also turn brown when they are ready for collection.
Origin and geographic distribution
Cucumis anguria is of African origin and it occurs wild in East and southern Africa. It has bitter fruits, but occasionally non-bitter types occur. Seeds were taken to the Americas with the slave trade, where the cultivated West Indian gherkin was developed. This edible, non-bitter type spread through the Caribbean, parts of Latin America and the southern United States. It can now be found in a semi-wild state as an escape from cultivation, and in some cases it appears to be an element of the indigenous flora. It is an invasive weed in parts of North America and in Australia, and a serious weed in peanut fields of the southern United States. The non-bitter edible form was reintroduced into Africa (e.g. Cape Verde, Senegal, Sierra Leone, DR Congo, Réunion, Madagascar, South Africa), where it is grown for its fruits. In Madagascar Cucumis anguria is probably not originally wild, but naturalized because it is localized around human habitations.
Traditional uses and benefits of using Wild cucumber
- The seeds are vermifuge.
- They are ground into fine flour, then made into an emulsion with water and eaten.
- It is then necessary to take a purge in order to expel the tapeworms or other parasites from the body.
- Cucumis anguria has been used in folk medicine to treat ailments of the stomach.
- Fruit is eaten to treat jaundice.
- Juice of the fruit, mixed with oil, is applied to contusions.
- Fruit is applied to hemorrhoids.
- An enema of the wild plant is used to treat stomach pains.
- Leaves, after being steeped in vinegar, are used against ringworm.
- Leaf juice preparation is applied to freckles.
- Decoction of the roots is used as a remedy for stomach troubles and to reduce edema.
- In America, medicinal uses are varied, including root decoction as a remedy for stomach trouble in Mexico, and to reduce edema in Cuba.
- Fruit is eaten to treat jaundice in Curaçao, and leaf juice preparations are applied to freckles in Cuba.
- Kidney problems are treated with a decoction in Colombia, where it is believed that the fruits eaten raw dissolve kidney stones.
- Fruit is applied to hemorrhoids in Cuba, and the leaves after being steeped in vinegar are used against ringworm.
Culinary Uses
- Fruit can be consumed raw, cooked or pickled.
- Fruit has a very agreeable cucumber flavor without any bitterness.
- It can be used in salads or as part of a savory dish.
- Fruit is frequently soaked in vinegar to make a pickle; it absorbs a large quantity of vinegar.
- Seed can also be consumed raw.
- Seed is rich in oil with a nutty flavor but very fiddly because it is rather small and covered with a fibrous seed coat.
- Young leaves can be cooked.
- Leaves of bitter forms are more likely to be eaten in Africa.
- Leaves of bitter forms of Cucumis anguria are cooked and eaten, in the same manner as pumpkin leaves.
- It is one of a range of edible wild greens, which are dried into cakes and stored for use during the dry season in Namibia.
- Fruits are eaten both fresh and dried in South Africa.
- Fruits are also relatively common as a table vegetable and they are used in soups and stews.
- Mature fruits are cooked as the main ingredient of a traditional soup called ‘maxixada’ in Brazil
- Immature fruit are used as fresh cucumbers.
- They may be eaten whole with the skin on when they are young, and can be sliced thin and used in salads like cucumbers.
- They can be used in casseroles and stews, and can be stir-fried with tomatoes, onion and garlic to make a ratatouille-like dish.
- They are commonly used in Brazil in a traditional hot-sour soup called “maxixada”, made with coconut milk and seafood.
- West Indian gherkins go well with other vegetables like okra, and are a good complementary ingredient to pork, chicken and beef.
Other Facts
- Bitter forms of the plant are occasionally used as a natural pesticide in stored crops.
- Juice of the fruit is supposedly used as an anti-feedant in granaries.
- Bitter forms of Cucumis anguria are sometimes used in Zimbabwe as a natural pesticide in stored crops.
- In Matabeleland (Zimbabwe) the fruit is used as a lure in rock and stick traps.
- An enema of the wild plant is used to treat stomach pain.
- Traditional medical practitioners consider the bitter fruit as poisonous and the juice of the fruit is used to treat septic wounds in livestock in Zimbabwe.
- Fruits may be produced within 60 days from time of planting.
- Single plant can produce 50 or more fruits.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=22360#null
https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/72028/
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/cucumis_anguria.htm
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=12546
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Cucumis+anguria
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CUAN
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cucumis_anguria
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-2746888
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Cucumis_anguria_(PROTA)
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/CUMAN
Comments
comments